Is Weight Extensive Or Intensive
1.2: Backdrop of Thing
- Folio ID
- 36961
Learning Objectives
- To split up physical from chemical properties and changes
All matter has physical and chemical properties. Physical properties are characteristics that scientists tin can measure without changing the composition of the sample nether report, such equally mass, color, and volume (the amount of space occupied past a sample). Chemical backdrop describe the characteristic ability of a substance to react to grade new substances; they include its flammability and susceptibility to corrosion. All samples of a pure substance have the same chemic and physical properties. For example, pure copper is ever a reddish-chocolate-brown solid (a physical property) and always dissolves in dilute nitric acid to produce a blue solution and a brown gas (a chemical property).
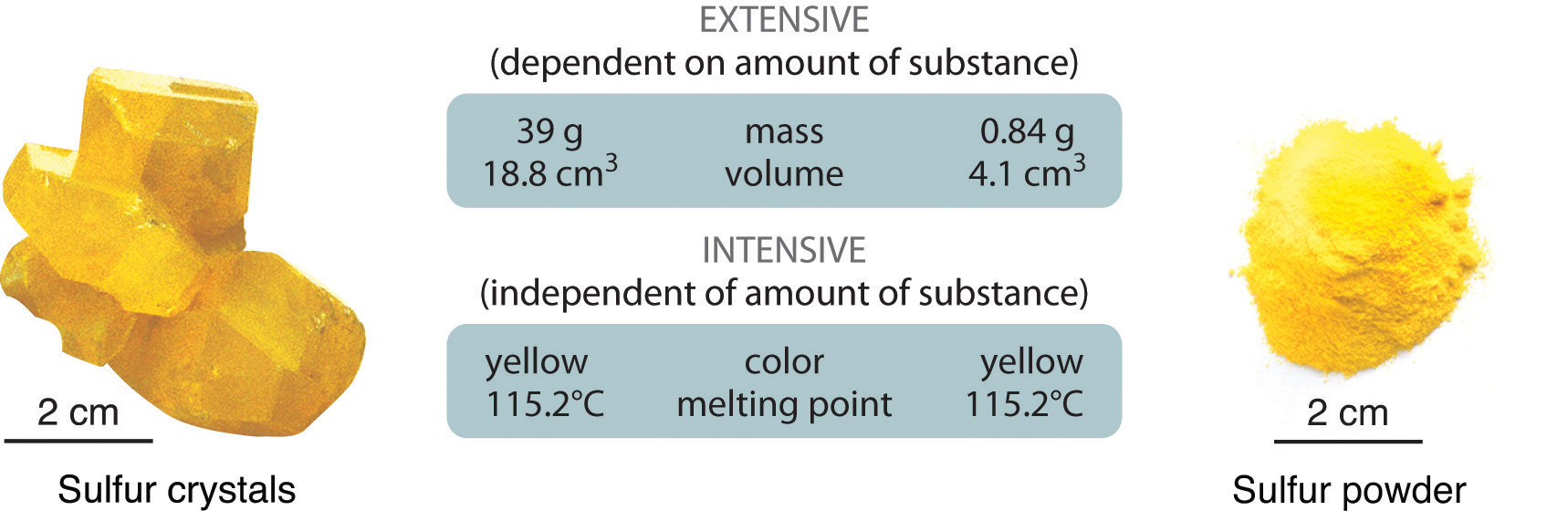
Concrete backdrop can be extensive or intensive. All-encompassing properties vary with the amount of the substance and include mass, weight, and volume. Intensive properties , in contrast, do not depend on the amount of the substance; they include color, melting point, boiling point, electrical conductivity, and concrete state at a given temperature. For case, elemental sulfur is a yellow crystalline solid that does non deport electricity and has a melting point of 115.ii°C, no matter what amount is examined (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Scientists commonly measure intensive properties to determine a substance'southward identity, whereas extensive properties convey information near the amount of the substance in a sample.
Although mass and book are both extensive backdrop, their ratio is an important intensive property chosen density (\(\rho\)). Density is defined as mass per unit of measurement volume and is usually expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm3). As mass increases in a given volume, density also increases. For example, pb, with its greater mass, has a far greater density than the same volume of air, just as a brick has a greater density than the aforementioned volume of Styrofoam. At a given temperature and pressure, the density of a pure substance is a constant:
\[density ={mass \over volume} \rightarrow \rho ={m \over v} \label{1.2.1}\]
Pure water, for instance, has a density of 0.998 g/cm3 at 25°C. The average densities of some common substances are in Tabular array \(\PageIndex{1}\). Notice that corn oil has a lower mass to volume ratio than water. This ways that when added to water, corn oil volition "float."
| Substance | Density at 25°C (one thousand/cm3) |
|---|---|
| blood | i.035 |
| body fat | 0.918 |
| whole milk | 1.030 |
| corn oil | 0.922 |
| mayonnaise | 0.910 |
| honey | 1.420 |
Physical Belongings and Change
Change in which the matter'south physical appearance is altered, but composition remains unchanged, eastward.g., a alter in state of thing. The three primary states of matter are: Solid, Liquid, Gas
- Solid is distinguished by a fixed construction. Its shape and book practice non change. In a solid, atoms are tightly packed together in a fixed arrangement.
- Liquid is distinguished past its malleable shape (is able to form into the shape of its container), but constant book. In a liquid, atoms are close together but non in a fixed arrangement.
- Gas is made up of atoms that are separate. However, different solid & liquid, a gas has no fixed shape and volume.
Different Definitions of Properties: https://youtu.be/n7UwjQJGh9Y
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\): Physical Change
When liquid water (\(H_2O\)) freezes into a solid country (ice), it appears inverse; Notwithstanding, this change is only physical every bit the the composition of the constituent molecules is the same: 11.xix% hydrogen and 88.81% oxygen by mass.

Chemical Properties and Modify
- Chemical Property is Whatsoever characteristic that gives a sample of matter the ability/inability to undergo a modify that alters its composition. Examples: Alkali metals react with water; Paper's power to fire.
- Chemic Alter is a Change in which one or more kinds of matter are transformed to new kinds of affair with altered compositions (or Chemical Reaction).
Example \(\PageIndex{2}\): Chemical Alter
The combustion of magnetisum metal is a chemic change (Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium Oxide):
\[ii Mg + O_2 \rightarrow 2 MgO\]
The rusting of iron is a chemical change (Iron + Oxygen → Iron Oxide/ Rust):
\[iv Fe + 3O_2 \rightarrow two Fe_2O_3\]
Using the components of composition and backdrop, we have the power to distinguish one sample of affair from the others.
Unlike Definitions of Changes: https://youtu.be/OiLaMHigCuo
References
- Petrucci, Bissonnette, Herring, Madura. Full general Chemistry: Principles and Modernistic Applications. Tenth ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458: Pearson Educational activity Inc., 2011.
- Cracolice, Peters. Nuts of introductory Chemical science An active Learning Approach. Second ed. Belmont, CA 94001:Brooks/Cole, 2007.
Contributors and Attributions
- Samantha Ma (UC Davis)
Is Weight Extensive Or Intensive,
Source: https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/University_of_California_Davis/UCD_Chem_002A/UCD_Chem_2A/Text/Unit_0:_Primer/1.2:_Properties_of_Matter
Posted by: ingramshament.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Is Weight Extensive Or Intensive"
Post a Comment